This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
Human beings need to be able to react to the world around them. The nervous system makes this possible. The nervous system is a network of specialised cells which carry electrical impulses very quickly from one place to another. It carries information from one part of your body to another at high speed. The nervous system not only carries information about changes in your surroundings, it also helps to coordinate all the different systems in your body.
The human body is made up of billions of cells. All of these cells need to work as a coordinated whole so that you can move around, eat, reproduce and carry out all the other characteristics of living organisms. The nervous system makes this possible.
Neurones are specialised nerve cells with adaptations which mean they can carry electrical impulses over long distances. Changes in the environment affect special nerve cells called sensory receptors. These send impulses along sensory neurones to coordination centres in the central nervous system made up of the brain and the spinal cord. Impulses are returned along motor neurones to trigger a response in an effector. The effector may be a muscle or a gland. It is the effector which allows the body to respond to any changes in the internal or external environment. Some of the nerve pathways of the body are under the conscious control of the brain but many are not.
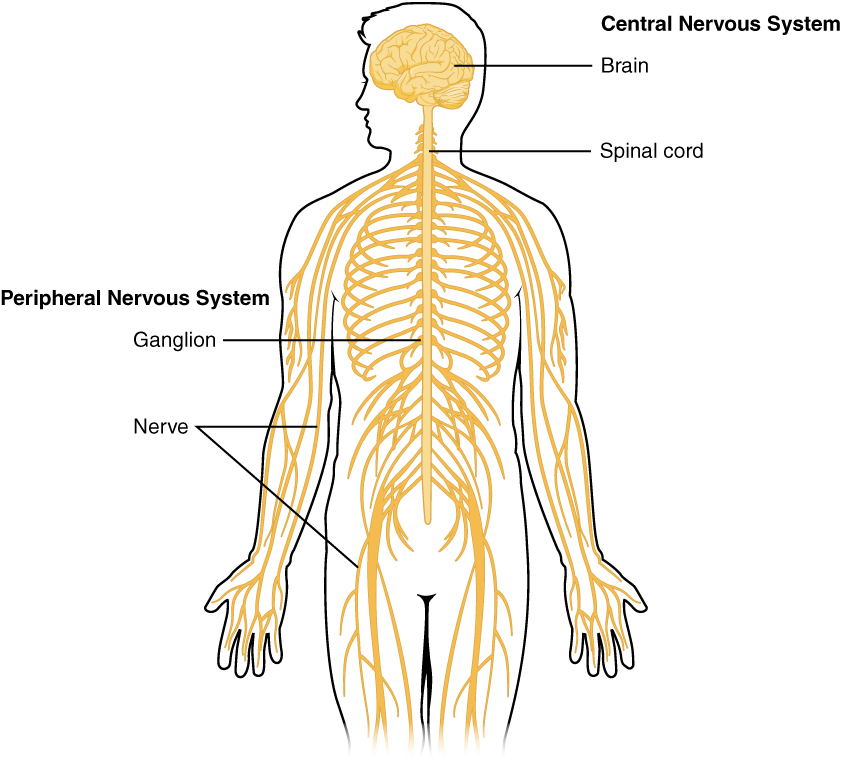
If the nervous system is damaged or diseased in any way it can cause big problems. Neurones are not easily repaired or replaced. A lot of research is taking place to find new ways of treating problems in the nervous system.
Sensory organs provide the body with vital information about changes in the world around you and the internal conditions of your body. For humans, sight is one of the key senses. The eye is a complex structure which enables you to see in colour and in 3D. We have a number of ingenious ways of correcting problems with the vision but there are still some conditions for which we do not yet have a solution.