This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
 Human biology
Human biology
 Physical education
Physical education
 Science
Science
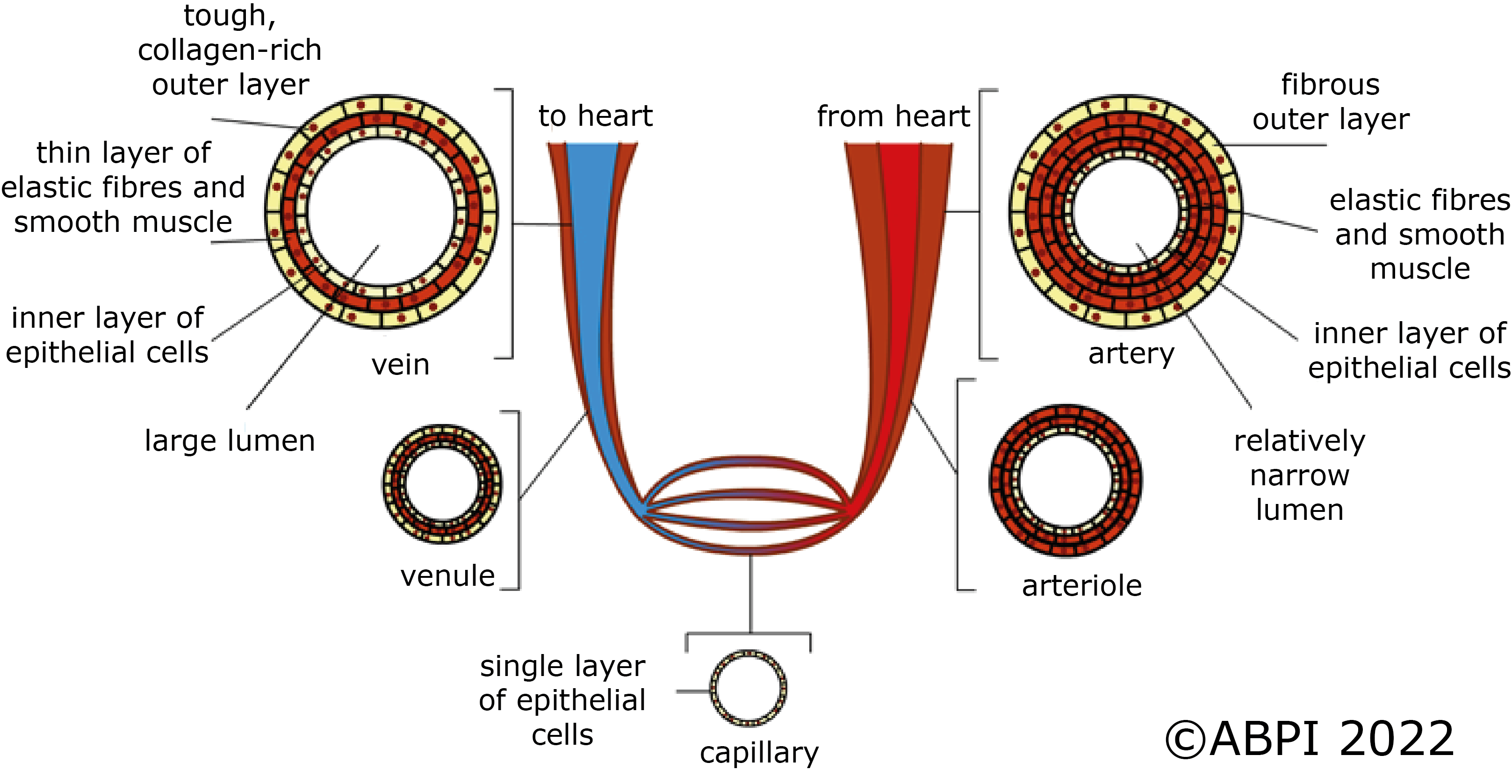
The blood pumped out of the heart is carried around the body in a 75,000 mile long transport network of blood vessels.
There are three main types of blood vessels - the arteries, the veins and the capillaries:
| Arteries | Veins | Capillaries |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
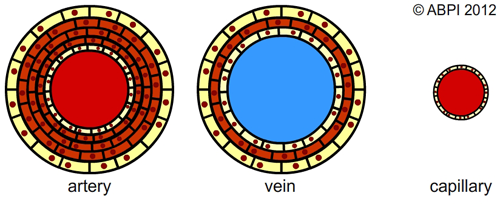
The structure of an artery, a vein and a capillary. As a diagram, the colours might not be accurate, and the scale is relative.
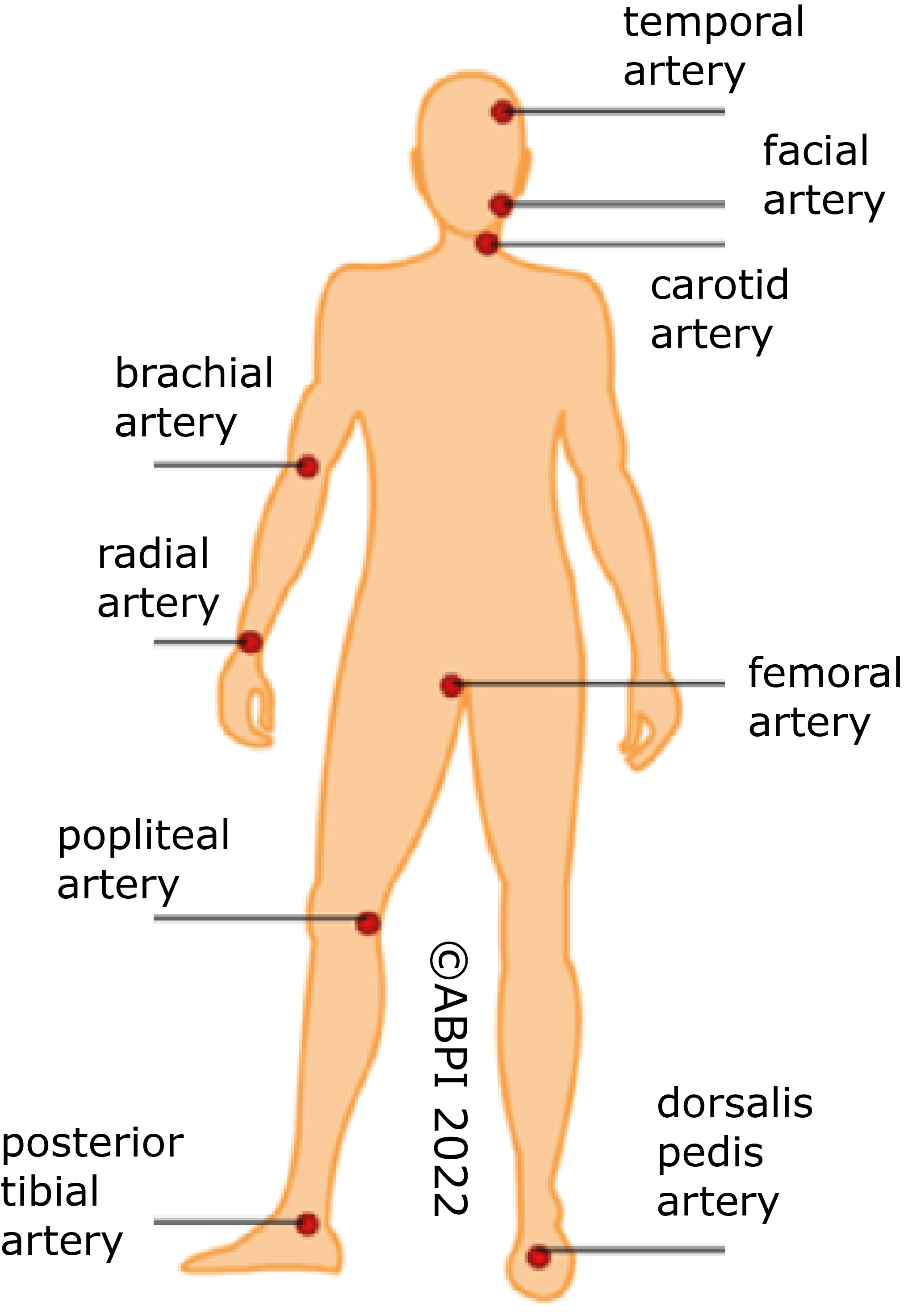
In some places in the body the arteries are relatively near the surface.
In these places you can feel the bulge as blood is forced out of the heart into the arteries followed by the return to normal shape.
This is known as the pulse.

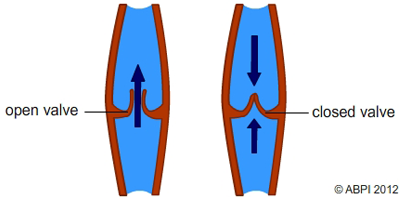
The blood travelling in the veins back to the heart is not under any great pressure. It is often squeezed in the right direction by the action of your muscles. A system of valves stops the blood flowing in the wrong direction. You can see how well the valves in your veins work if you experiment with the veins in your arm or hands.
It is in the capillaries that the exchange of substances takes place between the blood and the cells. The capillaries provide a massive surface area and thin walls for easy diffusion. Dissolved food and oxygen move out of the blood into the cells down a concentration gradient by diffusion. Carbon dioxide and urea move out of the cells into the blood in the same way.