This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
 Chemistry
Chemistry
 PSHE / Citizenship studies
PSHE / Citizenship studies
 Science
Science
Microorganisms are gaining resistance to antimicrobials - this is called antimicrobial resistance. This is often also called antibiotic resistance.
Microorganisms mutate in a random process called genetic drift. These mutations create microorganisms with a range of phenotypes. Some of these microorganisms will be resistant to antimicrobials.
Natural selection occurs when antimicrobials are used; antimicrobial medicines act as a selection pressure. Only resistant microbes can survive and reproduce. These microorganisms will pass on their resistance to offspring, passing on their selective advantage.
The diagram below summarises the development of antimicrobial or antibiotic resistance.
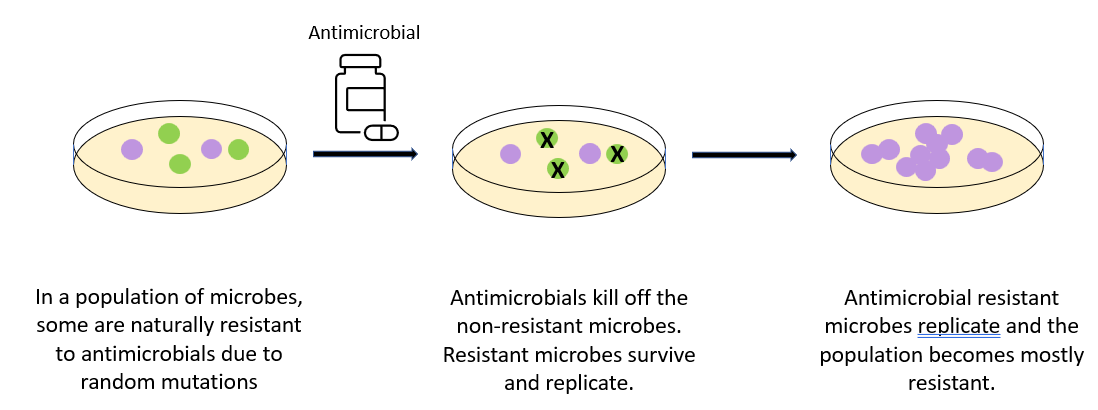
Once a microbe has developed resistance, it can pass it on to its offspring. Alternatively, bacteria can share plasmids that code for antibiotic resistance between each other via conjugation.
S. aureus divides every 30 minutes. If you start with one S. aureus bacterium, it would take only 5 hours for that single cell to grow into a colony of 1,024 cells. After 5 more hours, the population size will be 1,048,576 cells.
S. aureus has approximately 2.8 million nucleotide base pairs in its genome. If the mutation rate were 10-10 mutations per nucleotide base there would be 300 mutations in that population of cells within 10 hours!
Antimicrobial resistance development is an example of evolution via natural selection.
What are some other examples of natural selection?
