This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Human biology
Human biology
 Biology
Biology
 Physical education
Physical education
 PSHE / Citizenship studies
PSHE / Citizenship studies
Wherever you live and whatever you eat, the right balance of food is of enormous importance to your health and well-being. A balanced diet contains enough of the major food groups to supply the energy and nutrients you need to grow and maintain the cells, tissues and organs of your body.
Some types of food are needed in large amounts. These are the macronutrients which include carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. Other substances are just as important in our diets but are only needed in tiny amounts. They are the micronutrients and they include minerals and vitamins.
The main components of a balanced diet are:
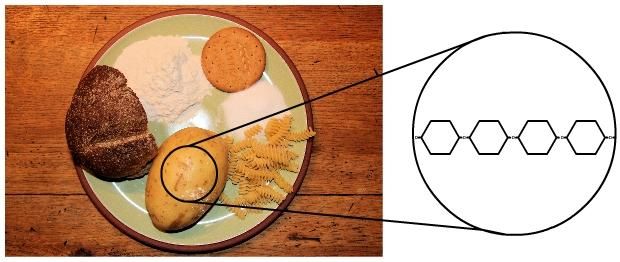
Carbohydrates provide us with easy-to-use energy. They contain the chemical elements of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. All carbohydrates are made up of units of sugar. Some carbohydrates contain only one sugar unit. The best known of these is glucose. Some carbohydrates are made of two sugar units joined together. Sucrose, the compound we call sugar in everyday life, is an example. Complex carbohydrates such as starch and cellulose are made up of long chains of sugar molecules joined together by condensation reactions.
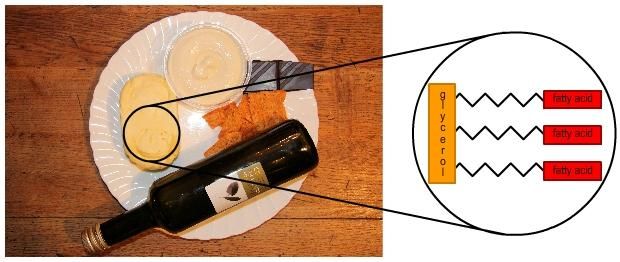
Lipids are fats (solids) and oils (liquids). The molecules contain a lot of energy and are a very important source of energy in your diet. They are also an important part of your cell membranes, as hormones and in your nervous system. Like carbohydrates they contain the chemical elements of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. A lipid is made up of three fatty acid molecules joined to a molecule of glycerol. The glycerol is always the same. It is the different fatty acids that affect the lipid and determine if it is a fat or an oil.
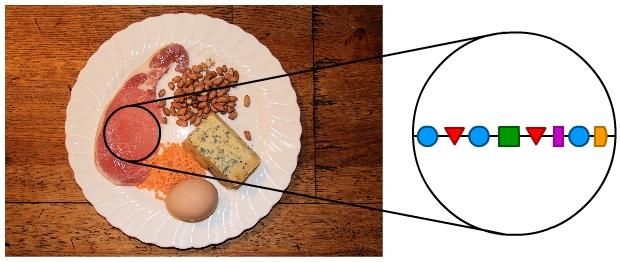
Proteins contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen and also nitrogen. They are used for building the cells and tissues of your body, and enzymes are also made of protein. Protein molecules are made up of long chains of amino acids joined together. There are 20 amino acids and different arrangements of these various amino acids give us all the different proteins. The long protein molecules are often folded or coiled to give them unique three-dimensional shapes.
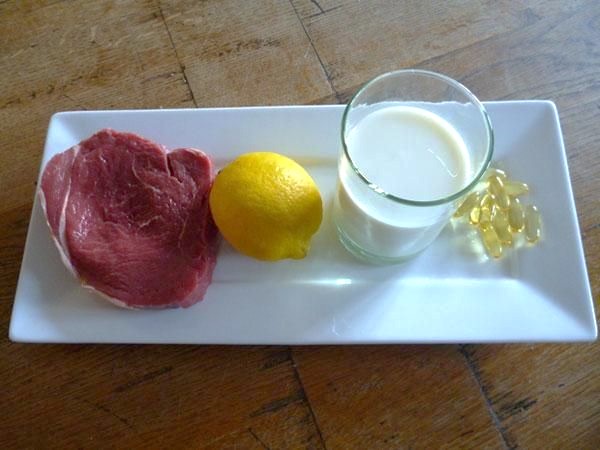
Minerals and vitamins are needed in your body in very tiny amounts, but they are vital for your body to grow and function healthily. A lack of them in the diet can lead to many different deficiency diseases.
Minerals include:
Vitamins include:

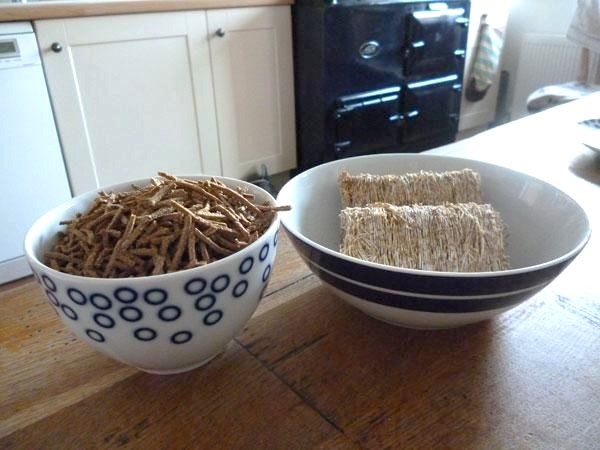
Fibre (also known as roughage) is material which you cannot digest - for example the cellulose in plant cell walls. It does not get broken down, but it is very important for the healthy working of the digestive system. It provides bulk which allows the muscles to contract and move food through the digestive system steadily.
