This topic takes on average 45 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Human biology
Human biology
In sexual reproduction, both meiosis and mitosis are needed to produce new, genetically unique individuals.
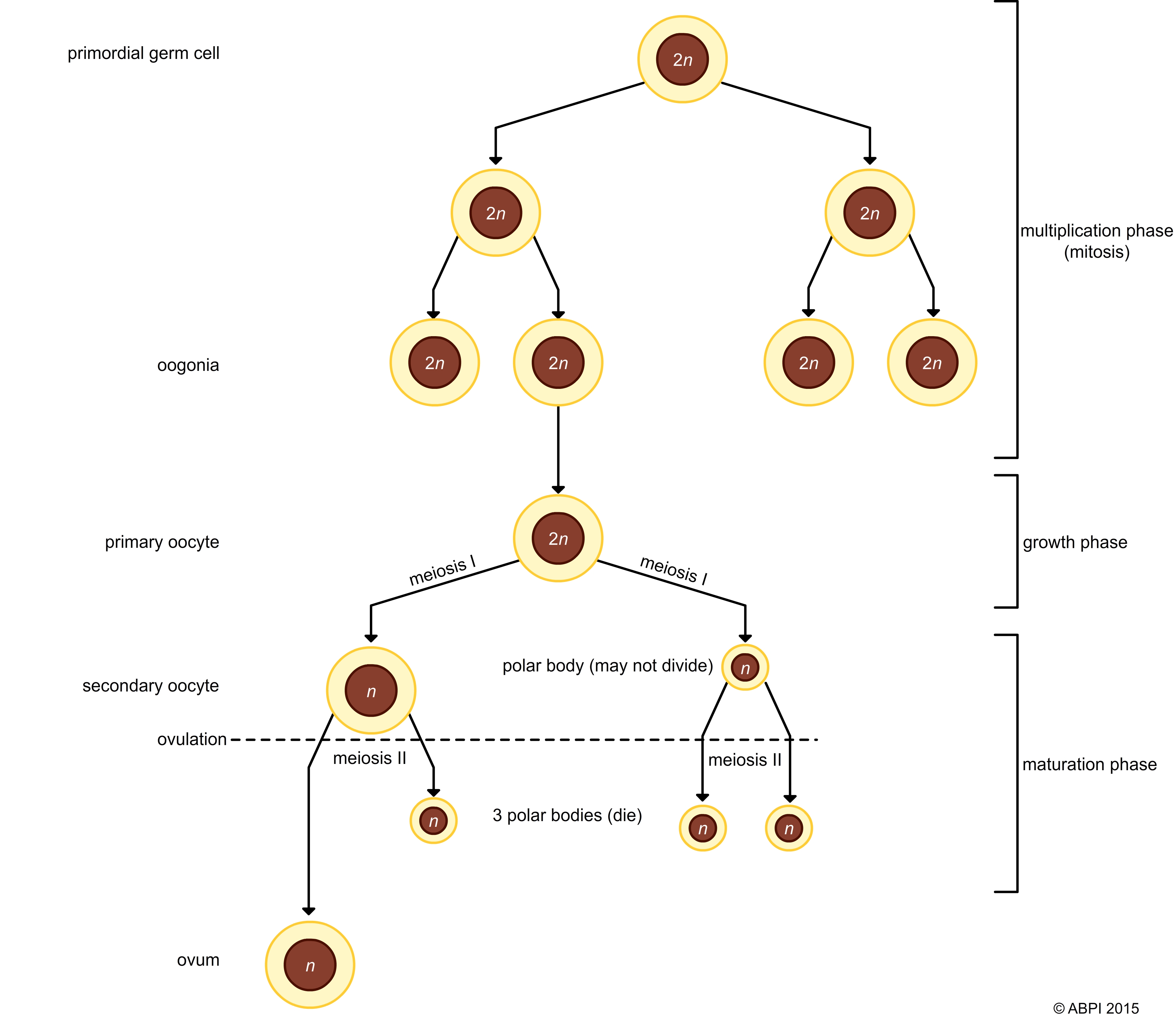
Meiosis, the cell division that halves the number of chromosomes in a cell, is a key part of gametogenesis but it is not the whole story. The process of making eggs or sperm in mammals, or ovules and pollen in plants, involves more than meiosis.
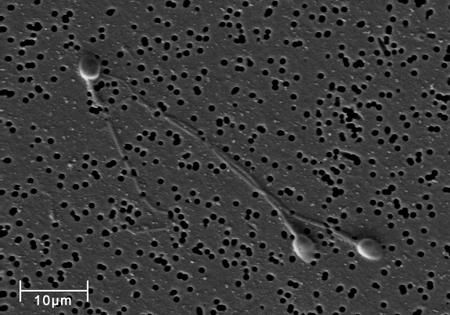
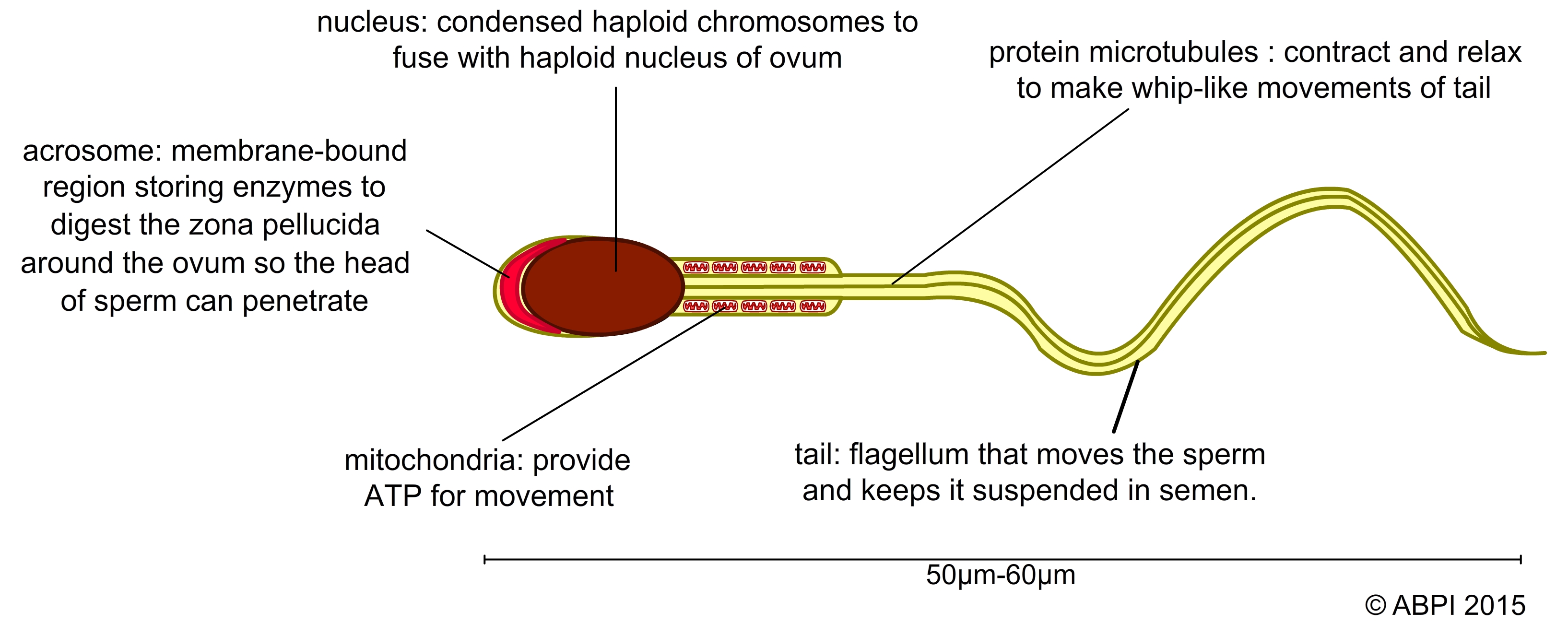
In mammals, the male produces large numbers of very small, mobile gametes called spermatozoa (sperm). The sperm carry a haploid nucleus. They contain many mitochondria to generate the ATP needed for the contraction of the specialised proteins in the tail. This lashes from side to side to help keep the sperm suspended in the semen and moving when released into the female reproductive tract.
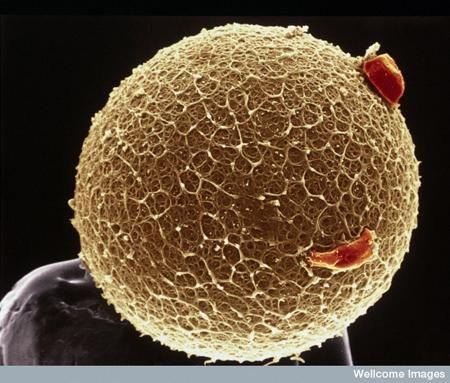
Scanning electron micrograph of mammalian/human ovum (Photo credit: Wellcome Images. Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic license)
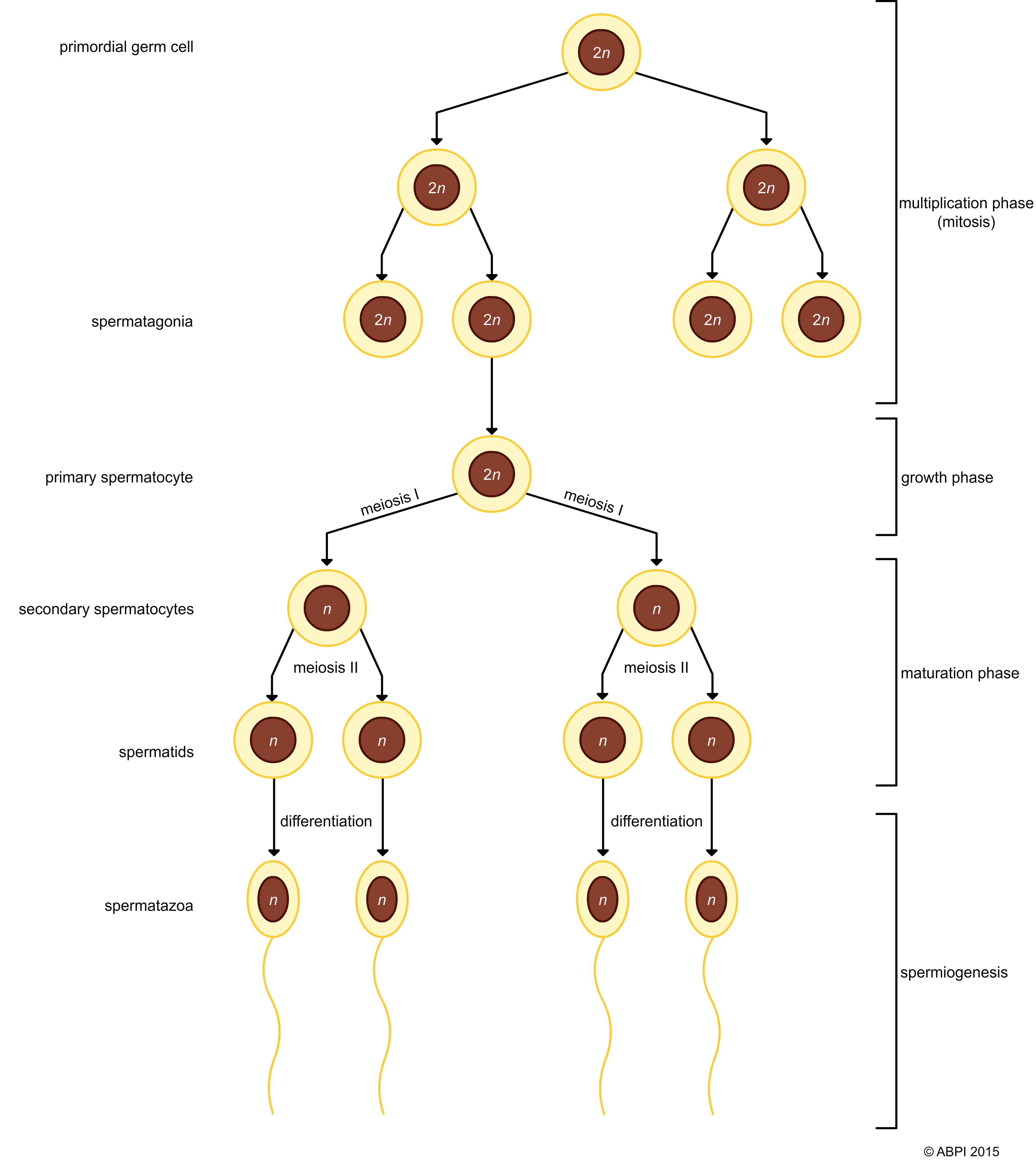
Spermatogenesis is the production of spermatozoa and it starts in the human male at puberty. Sperm production continues throughout life, although the numbers fall and the quality of the sperm declines with age. Many more mutations appear in the sperm as a man gets older, making the sperm less fertile and increasing the chance of passing on mutated genes to the offspring.
The testes contain primordial germ cells. They divide both by mitosis and meiosis to produce millions of spermatozoa every single day. Each primordial germ cell produces many spermatozoa.
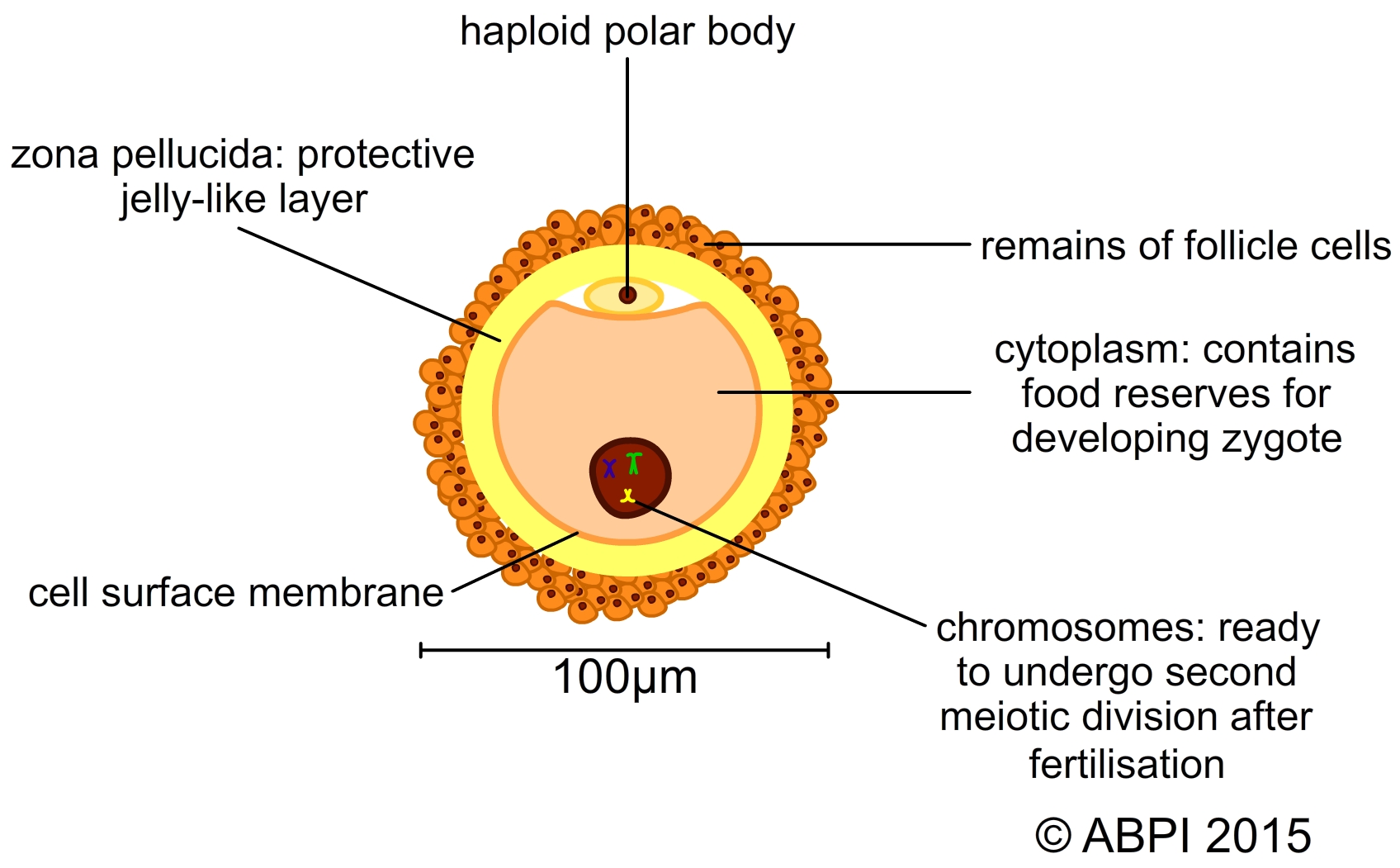
Oogenesis is the formation of ova. All of the primordial germ cells a girl will ever possess are present in her ovary at birth. Each primordial germ cell will only ever produce one ovum. Because each ovum contains so much more material than a sperm it would be a waste of resources to make too many.