This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Science
Science
 Human biology
Human biology
Historically, the Bohr-Rutherford diagram was used to describe atoms, with electrons orbiting the nucleus in energy levels or electron shells like the planets orbiting the sun. In fact, this model for the atom is not correct!
Instead, electrons inhabit areas of space called orbitals. As electrons do not follow a set path or orbit, orbitals are regions of space where the electron is most probably found.
Take the Hydrogen atom and imagine how it would look if you determined the position of its one electron and plotted them at different points in time:
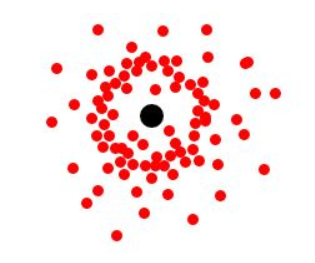
The dots surround the nucleus spherically, with a higher density of dots at some distance from the nucleus. Therefore, the electron is most probably found in a spherical space surrounding the nucleus with a higher probability at an undescribed distance from the nucleus. Do not think this higher probability region of space suggests some type of orbit or is the surface of the sphere – it is not. It is included in the above diagram for completeness, but explanation of this higher probability region in space is beyond the scope of A-level. Remember: The electron may be found anywhere within the spherical space. As this is a spherical orbital, it is called an s-orbital. Therefore, the Hydrogen electron occupies the 1s orbital. The “1” denotes that the s-orbital is within the lowest energy level or the electron shell closest to the nucleus. Increasing electron shells, 2, 3, 4, …, etc. are found at increasingly higher energies with increasing distance from the nucleus. Orbitals may be thought of as subshells within these electron shells, but more on that later.